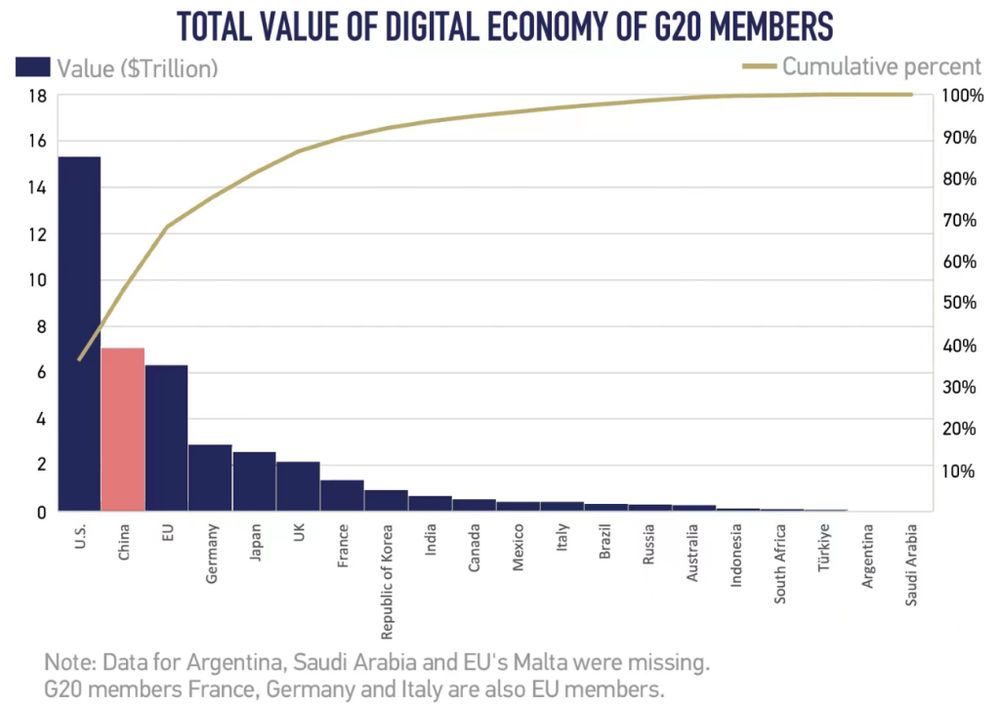
- China’s Digital Economy ranks second in the world, after the U.S.
- The State Council of China, as outlined in the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025), continues to prioritise the growth of the digital economy with the goal of contributing 10% to the national GDP by 2025
- As one of the first countries to adopt a central bank digital currency (CBDC), China saw the amount of digital yuan (e-CNY) in circulation reach US$2 billion (RMB13.6 billion) at the end of December 2022 [1]
In this world of digitalisation, China is a leading investor and adopter of digital technologies. Being more digitised than many appreciate, it is home to some of the largest digital companies in the world, like Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent and more. Hence, it is not surprising that China could lead the world’s digital frontier, given the profound growth rate of its digital economy.
But how did China become one of the world’s leading technology players? To understand this, we must first understand what a digital economy is and how it works.promoting technological innovation.

What is a digital economy?
A digital economy is the segment of the economy driven by millions of daily interactions between individuals, businesses, devices, data and processes, all of which occur online. Without this hyperconnectivity between people, organisations and machines—enabled by the Internet, mobile technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT) [2] —the digital economy would not be the big, thriving thing it is today.
Three parameters that define a digital economy are [3]:
- Infrastructure: Businesses with expert human resources available for deployment and evolving technological resources.
- Technology and innovation: Computer applications, online tools and digital platforms that facilitate business activities.
- E-commerce: Sales of goods and services online.
The importance of the digital economy in the current time
The digital economy is transformative for both businesses and customers. While people are empowered in ways that change and impact their behavior as consumers, businesses can operate within entirely new realms of opportunity. Digital economy overcomes the limitations of a traditional economy, for example, in production, marketing and commerce. On top of those, it also helps businesses to:
- Access entirely new markets and customers, thanks to the global reach of the Internet.
- Reduce costs by replacing outmoded marketing methods, production and distribution with effective digital ones.
- Achieve greater efficiency through superior tools, technologies and data.
- Generate new jobs, such as digital marketing, big data analysis and data mining, due to the demands of new businesses and start-ups.
- Innovate better, thanks to the experimentation with concepts and technologies that becomes necessary to produce, market and sell products and services online [4].
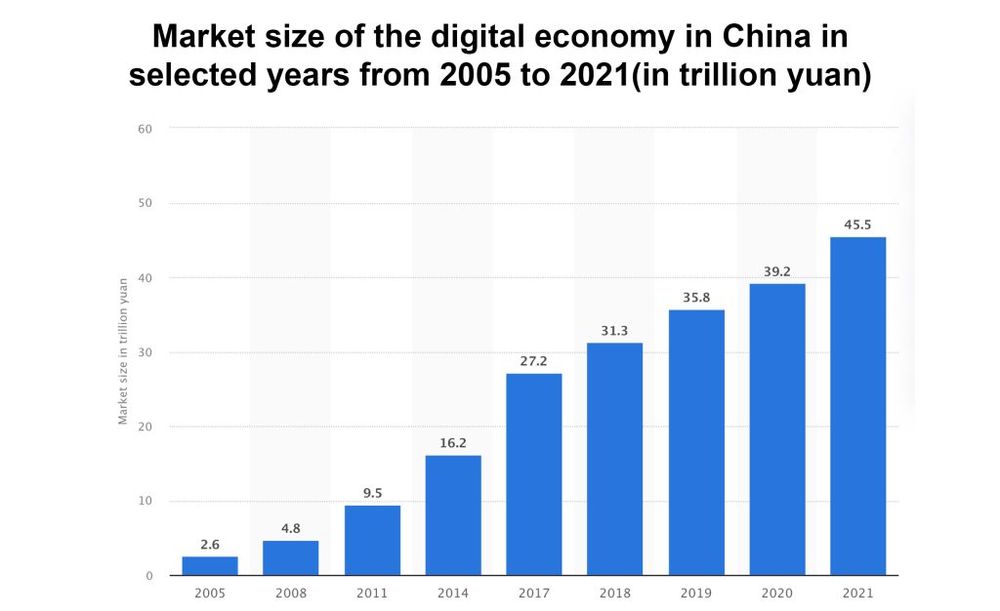
China’s place in the global digital economy
According to a white paper published by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT) and figures from the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), China is one of the world’s largest investors and adopters of digital technologies.7
Based on the valuation of digital economies, it follows a close second to the U.S. [5] Observers note that the diligent and consistent expansion of digital infrastructure construction has accompanied the explosion of China’s digital economy. This is a natural corollary as the technologies that support the digital economy are precisely these components—big data, cloud computing, IoT, blockchain, artificial intelligence, 5G communications and so on [6].
One of China’s strategies to increase the digital economy’s contribution to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is to increase internet connections and speeds. As of March 2022, China has had 1.43 million 5G base stations and over 500 million 5G customers. By 2025, China aims to own approximately 30% of the world’s total data volume [7].
Significant sectoral contributions to China’s digital economy
Digitalisation-industrialisation [8]
In a bid for greater efficiency, Chinese industrial corporations have been deploying digital tools more frequently, thus making the most of the nation’s burgeoning digital infrastructure and favorable legislation. Utilising cutting-edge information and communication technologies — such as 5G, IoT, big data analytics, augmented or virtual reality and artificial intelligence — is a key component of Chinese industrial corporations’ digitalisation strategy.
For example, Midea Group Co., Ltd. has successfully reduced data latency to milliseconds. In addition, the core data assets created have saved costs by over 20% and increased efficiency by over 50% in some areas of operation.
Yankuang Energy Group Company Limited, on the other hand, has effectively used 5G technology and robots to cut down data delays from three-four seconds to milliseconds, thus enabling the deployment of remote-controlled mining without underground workers. This is an example of how the digital economy enables not just cost-saving but also life-saving changes.
Financial Sector
The financial sector has always played a fundamental role in China and the digital economy further leverages that. Cloud computing services provide a variety of software and digital resources as on-demand services to financial companies. To cite one example, Huawei delivers dependable financial infrastructure, creates intelligent architecture and supports business innovation through its reliable networks, thereby upping the digital value of the banking sector.
Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing sector continues to be the backbone of the ‘real’ economy. However, the digital economy can expand the bounds of the possible in this sector as well. For instance, Tencent WeMake, an industrial internet platform, enables businesses to create data-driven intelligent factories that can automatically alter operations on the shop floor. Both human decision-making and operational efficiency are therefore enhanced through the modules and platforms of the digital economy [9].
The role of the Chinese government in developing the digital economy
The digital economy is a consistent beneficiary of China’s national development strategy. Under the 14th Five-Year Plan, China aims to skill-build in strategic areas such as quantum information, communications, integrated circuits, sensors and blockchain, in addition to promoting technologies like 6G.
The State Council has established clear-cut goals for 2025, including a hike in the proportion of the national GDP that comes from the digital economy — from 7.8% in 2020 to 10% in 2025. The number of people using gigabit broadband (currently the fastest connection speed available) is projected to rise from 6.4 million in 2020 to 60 million in 2025, along with accelerated data center building [10].

Initiatives to boost the digital economy in China
Chinese Digital Currency (e-CNY)
China’s digital currency, the digital yuan or e-CNY, was the first state-led effort to implement a digitised payment mechanism. Adopting the digital yuan is seen as a timely step for public payment scenarios, such as between enterprises and the state, where security and stability depend on bank accounts [11]. At the end of December 2022, the amount of e-CNY in circulation reach US$2 billion (RMB13.6 billion) [12].
China and G20
When China held the rotating presidency of G20 in 2016, the digital economy was highlighted as a key theme for the first time at the summit in Hangzhou. A digital economy encourages innovation, partnership, synergy, flexibility, inclusiveness and an open and empowering business environment, with a free flow of information for greater economic growth and security.
Acting by example, the G20 member countries responsible for over 85% of the world’s GDP, 75% of its trade and 60% of its population are taking the lead in the future of the digital economy. As a result, the total value of digital economies across 47 large countries worldwide jumped to US$38 trillion in 2021, up 16% from 2020 and accounted for 45% of their total GDP.
Collaboration with International Tech Giants
In June 2022, Siemens set up its first Smart Infrastructure Digitalisation Enablement Center in China as a starting point to explore collaboration with domestic firms in smart infrastructure. IBM, too, has been proactively assisting Chinese businesses with their digital transformation. For instance, the company helped China and Brazil with digital technology to maintain the ecosystem of the Amazon jungle [13].
International partnerships further boost the growth of China’s digital economy
Saudi Arabia and China
A strategic collaboration between these two countries has set up a framework for bilateral cooperation in areas of communications and information technology as part of developing digital economies in the respective nations. Key objectives are to encourage research and innovation in the field of emerging technologies, enhance specific aspects of communications infrastructure and nurture the development of digital entrepreneurship by employing new business models like financial technology and e-commerce [14].
Indonesia and China
At the 2022 G20 summit in Bali, the two countries signed a deal to bring better internet connectivity to hundreds of remote islands in Indonesia. Being a large country where e-commerce is booming, China has pledged to assist Indonesia in developing its digital economy, which is hamstrung not only by the lack of knowledge needed to sell products online but also because of unreliable Internet services [15].
To conclude, China’s digital economy has already shown tangible gains, creating jobs and generating wealth across the country. With its speed of technological advancement and adoption, China is undeniably poised to take even greater strides in this direction.
References
- [1] & [12] CoinDeck: China Includes Digital Yuan in Cash Circulation Data for First Time
- [2] Deloitte: What is Digital Economy?
- [3] Santander: The Digital Economy: What it is and Why it’s the Future of Business
- [4] FeeDough: What Is Digital Economy? – Importance, Types, Examples
- [5], [6], [7] & [11] China Briefing: Understanding China’s Digital Economy: Policies, Opportunities, and Challenges
- [8] FitchRating: Chinese Digital Economy’s Industrial Penetration Set to Rise
- [9] The Diplomat: Will China’s Technology Be a Game-Changer in the Post-Pandemic Era?
- [10] Reuters: China’s Cabinet Says it Will Promote Transformation of Digital Economy
- [13] CGTN: Digital Economy Becomes New Growth Engine for China and Other G20 Members
- [14] Gulf Business: Saudi Arabia and China Strengthen Partnership in Digital Economy
- [15] South China Morning Post: China to Help Indonesia Build Digital Economy as E-commerce Sweeps Archipelago